How is AI Used in Manufacturing?

With a background that includes experience at EY and Wipro, she’s been a trusted advisor for clients seeking innovative solutions. Her expertise in unraveling complex business challenges and crafting tailored solutions has propelled organizations to new heights. I have proven my adaptability by consistently meeting the demands of creating responsive and scalable applications. Also seamlessly integrating complex workflows and data sources, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and driving sustainable business growth. Network experts can help de-risk your company’s adoption of AI and other advanced technologies via hands-on technical assistance, as well as connecting you with grants, awards and other funding sources.
Connected cars can detect the changing in road conditions, optimize deliveries and monitor the roads for accidents and emergency services so the result is more efficient deliveries and reduced accidents. Explore the five steps you need to take to get started with digital twins and get insight into successful digital twin initiatives. Conversely, AI can work round the clock performing tasks with a higher degree of accuracy. It doesn’t get tired or distracted, it doesn’t make mistakes or get injured, and it can work in conditions (such as in the dark or cold) that we humans would balk at.
Top 10 Use Cases of AI in Manufacturing
AI steps in as a cognitive assistant, providing real-time insights, recommendations, and data analysis. Workers can make informed decisions swiftly, leveraging AI’s computational power to handle data-intensive tasks. At the core of AI lies machine learning, a field that empowers machines to learn patterns and insights from data.
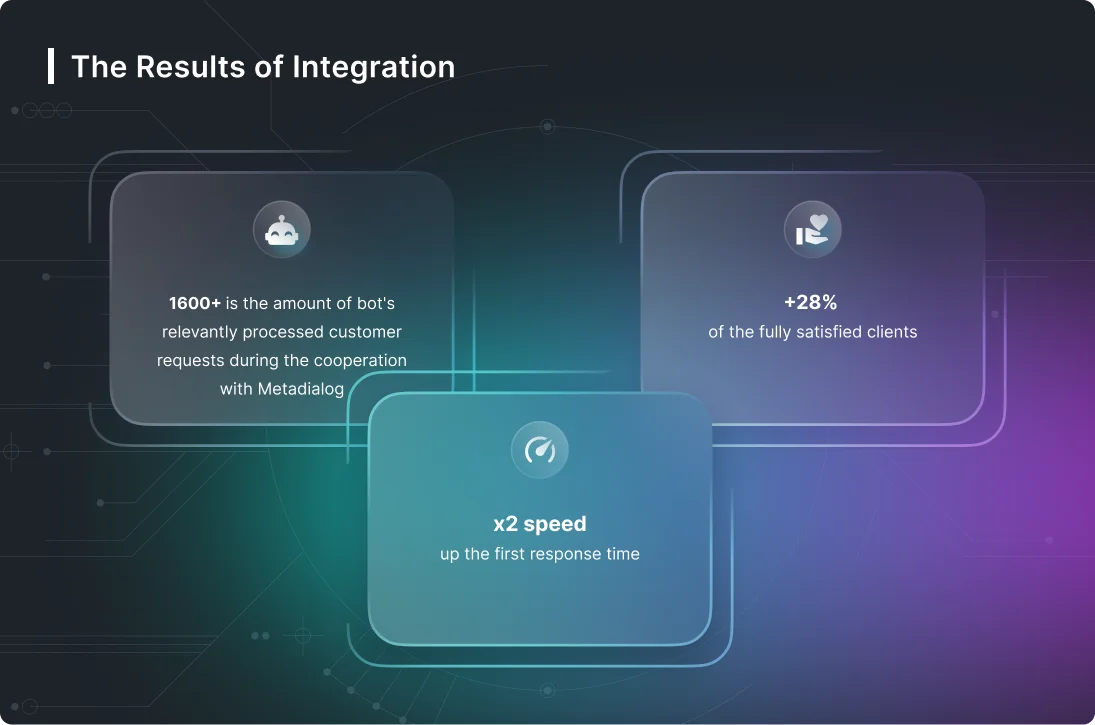
A real-world example of this concept is DRAMA (Digital Reconfigurable Additive Manufacturing facilities for Aerospace), a £14.3 million ($19.4 million) collaborative research project started in November 2017. Developers are building an additive manufacturing “knowledge base” to aid in technology and process adoption. One impactful application of AI and ML in manufacturing is the use of robotic process automation (RPA) for paperwork automation.
Future Prospects and Challenges
This can be extremely beneficial for closely supervised industries like automotive and aerospace that must meet stringent quality standards set by regulatory agencies. Supported by the data collected from industrial sensors, AI helps to eliminate unplanned downtime and optimize process effectiveness. With AI examining equipment performance data, not only are impending maintenance issues detected, but potential inefficiencies are identified as well. This helps to fine-tune equipment to ensure optimal operation and maximum output at peak quality.

Strukton Rail reported that predictive maintenance made it possible to halve the number of technical failures. The company is going to expand POSS with a forecasting tool to predict impending failures and such application of AI-based predictive maintenance can be suitable not only for the Dutch railway, but others as well. In October 2019, Microsoft reported artificial intelligence helped manufacturing companies outperform rivals stating that manufacturers adopting AI perform 12 percent better than their competitors. Therefore, we are likely to see an upsurge in AI-based technologies in manufacturing along with the advent of new high-pay jobs in this arena. It predicts demand, adjusts stock levels between locations, and manages inventory across a complex global supply chain. In short, machines on the factory floor can now communicate with one another and operate with an impressive degree of autonomy.
Optimize scheduled maintenance based on unscheduled downtime with predictions for mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). These three technologies are artificial intelligence techniques utilized in the manufacturing industry for many different solutions. Artificial intelligence studies ways that machines can process information and make decisions without human intervention. A popular way to think about this is that the goal of AI is to mimic the way that humans think, but this isn’t necessarily the case. Although humans are much more efficient at performing certain tasks, they aren’t perfect.

Keep reading to see five ways that artificial intelligence is being used in manufacturing today. In this look at AI in the manufacturing industry, we’ll discuss what artificial intelligence is, how it plays a role in manufacturing, and review several examples of how AI is used in manufacturing. Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer. The Motley Fool reaches millions of people every month through our premium investing solutions, free guidance and market analysis on Fool.com, top-rated podcasts, and non-profit The Motley Fool Foundation. Manufacturing is one of the highest-risk industrial sectors to be working in with more than 3,000 major injuries and nine fatalities occurring each year. The involvement of robots in high-risk jobs can help manufacturers reduce unwanted accidents.
By leveraging machine learning algorithms, manufacturers can gather insights from market trends, customer preferences, and competitor analysis. This empowers them to make data-driven decisions and design products that align with market demands. Moreover, the use of AI in the manufacturing industry has also revolutionized predictive maintenance.
- They say forewarned is forearmed – and in the manufacturing industry, this expression is very relatable.
- If a label is missing or illegible, an ejector removes the offending product without stopping the assembly line.
- A digital twin is a digital representation of a physical product in all its aspects.
- Manufacturers use AI to analyze data from sensors and machinery on the factory floor in order to understand how and when failures and breakdowns are likely to occur.
While reactive and preventive maintenance help decrease or just prevent failures, predictive maintenance uses models to forecast when a specific asset is about to have a component fail. Department of Energy data, predictive maintenance can reduce machinery downtime by 35% to 45%. However, the most important role of AI in manufacturing is its ability to help people and machines work synergistically. For discrete manufacturing organizations, this is a win-win; technology-enabled people and processes lead to greater efficiency, productivity and safety, among other benefits. Cloud-based machine learning – like Azure’s Cognitive Services – is allowing manufacturers to streamline communication between their many branches. Data collected on one production line can be interpreted and shared with other branches to automate material provision, maintenance and other previously manual undertakings.
For instance, an electronics manufacturer can launch AI-driven robots to automate the assembly of intricate circuit boards, resulting in a significant reduction in errors and a substantial increase in production output. In this exploration of AI in manufacturing, we will dive deep into how these applications are reshaping the industry. The utilization of AI for quality control, the implementation of predictive maintenance strategies, and the optimization of supply chains exemplify the transformative potential of this technology.
They can also carry out quality control inspections using computer vision-enabled cameras. Examples of possible upsides include increased productivity, decreased expenses, enhanced quality, and decreased downtime. Big factories are just some of the ones that can benefit from this technology. Many smaller businesses need to realise how easy it is to get their hands on high-value, low-cost AI solutions. They say forewarned is forearmed – and in the manufacturing industry, this expression is very relatable.

Manufacturers can now train deep learning models so that they can find any potential defects in equipment and relay this information in real-time so that preventative action can be taken. Once the realm of science fiction, artificial intelligence (AI) has made its foray into our lives and businesses in recent years. AI quickly interprets and learns from data to provide predictions and identify trends. Manufacturers generate more data than any other business sector, but they also waste the most data.
Companies are currently finding it challenging to fill specialized roles; some provide advanced training to their expert staffers. BMWs are known to be sleek and fast automobiles, and now thanks to AI, they have the production capabilities to match their design. BMW Group utilizes AI in manufacturing solutions to perform monotonous tasks that used to require human intervention, including quality control, logistics coordination, and virtual layout planning. Traditionally machines are required to be repaired after a particular interval of time or usage for preventive maintenance processes. However, it still results in significant equipment failure instances resulting in idle workers, lost revenues, and customer trust loss.
Most manufacturers have experienced the pain of being over- or under-stocked at crucial moments, leaving money on the table and/or indirectly pushing customers into the arms of competitors. Inventory management has so many moving parts (shifting demand, omnichannel sales, material availability, production capacity, etc.) that humans can’t get right all the time. Increasingly, however, AI isn’t being used to improve sales rep performance but replace reps altogether. With an AI algorithm integrated into your website, buyers can configure and buy even the most complex, configurable products without human interaction. Not only does this reduce costs for the seller, but it dramatically improves CX for most buyers who prefer self-serve over human interaction. In fact, AI application increases employee productivity across the board by providing critical insights and automating repetitive processes.

Afterwards, the machine learning network analyzed the received data and predicted the moment of a break. Three-year data was collected and analyzed from channels inside the furnace and close to the panels. The final quality of the device directly depends on detecting defects on a PCBs (Printed Circuit Board) during the pre-production phase of manufacturing.

Read more about https://www.metadialog.com/ here.
